A business model outlines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. It details the products or services offered, target market, and revenue streams. It includes the company’s strategy for growth and sustainability.
Business Model having a blueprint that transforms your innovative idea into a thriving enterprise. A well-crafted business model is your key to understanding how to create, deliver, and capture value. It guides you in identifying target markets, defining unique value propositions, and generating sustainable revenue. With the right business model, you can turn your vision into reality and outpace competitors.
A business model is more than just a plan; it’s a strategic framework that defines how a company operates and makes money. It encompasses everything from product development and marketing strategies to customer engagement and revenue generation. By clearly outlining key activities, resources, and partnerships, a business model helps organizations align their operations with their goals. It also provides a roadmap for scalability and adaptation in a constantly changing market.
Winning Business Model
You have a brilliant idea for a new product or service. The next crucial step is developing a business model that will allow your startup to successfully bring that idea to market and turn it into a thriving enterprise. Getting the business model right from the start is absolutely essential.
A well-designed business model serves as a blueprint for your operations, mapping out how your startup will create value for customers, capture a share of that value as revenue, and sustain a competitive advantage over time. It defines your core products/services, target customers, revenue streams, costs, key activities, resources, partners, marketing channels, and more.
Without a sound business model underlying your efforts, even the most ingenious startup idea will likely stumble and fail. That’s why savvy entrepreneurs put serious thought into crafting a business model that positions their startup for profitability and growth right out of the gate.This article will walk you through the key components to include in your startup’s business model and factors to consider for each one.
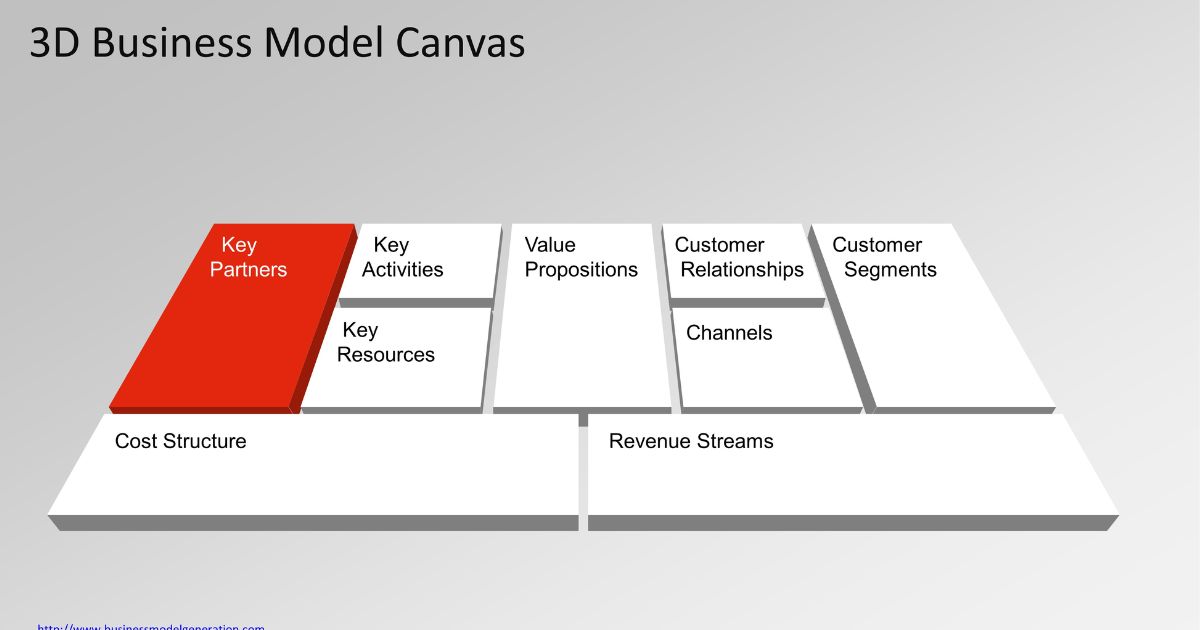
The 9 Key Components of a Startup Business Model
There are 9 essential building blocks that make up a comprehensive business model, according to the framework popularized by Alexander Osterwalder’s book Business Model Generation. We’ll examine each one in turn:
Customer Segments
The first step is clearly defining who your target customers are. Which groups or segments of people/organizations does your startup aim to serve? Get as specific as possible on the demographics, behaviors, and other traits. Different customer segments have different needs, so you may end up needing slightly different offerings for different groups.
Value Propositions
the value you plan to deliver to those customer segments. What core products and services will you offer, and what key problems or needs will they satisfy for your customers? How will your value propositions distinguish you from the competition? This is where you crystallize the unique benefits your startup provides.
Channels
Consider how you will connect and communicate with your customer segments to deliver your value propositions. What sales channels, communication channels, and distribution channels make the most sense? This could include a website, mobile app, retail locations, sales team, advertisements, and more. Develop a clear channel strategy.
Customer Relationships
The types of relationships you want to establish and maintain with each customer segment. Will the relationship be heavily automated or will you provide dedicated personal assistance? What mechanisms can you put in place to maximize customer acquisition, retention, and loyalty over time?
Revenue Streams
This is where you define how your startup will actually make money by capturing value from customers. What pricing mechanisms will you use (subscription, pay-per-use, etc.)? What are customers willing to pay for each stream? Ensure your revenue streams are aligned with your value propositions.
Key Resources
The key resources required to create and sustain your value propositions, customer relationships, and revenue streams. This includes people, technology, intellectual property, facilities, cash/capital and more. Obtaining these critical resources should be a top priority.
Key Activities
Likewise, map out the key activities involved in executing your business model, from production and logistics to marketing, IT systems, hiring and beyond. This paints a picture of your startup’s core competencies and workflows.
Key Partnerships
Most startups rely on partnerships and strategic alliances with certain suppliers, technology firms, research institutions, and others. Identify any key partners you’ll need to work with and the motivations for partnering with them.
Cost Structure
Finally, your business model should account for all the major fixed and variable costs involved in operating your business based on the other components outlined above. This calculation of your cost structure is critical for determining pricing, profit potential, fundraising needs, and overall viability.
Designing Your Unique Business Model Now that we’ve covered the 9 key components, let’s discuss some overarching principles and strategies to consider when piecing together your startup’s tailored business model.
Proposition
Focus on a clear, compelling value proposition. The core value proposition you offer customers is the heart of your business model. Everything else flows from defining a clear, differentiated value proposition that genuinely solves a need better than alternatives. Spend serious time honing this piece first.
Emphasize recurring revenue streams. Ideally, your business model should involve recurring revenue streams from customers rather than purely one-off transactions. Many of today’s most successful startups utilize subscription-based or consumption-based pricing that provides reliable, predictable income. This could mean a monthly subscription fee, pay-per-use, or other recurring pricing mechanism tied to delivering ongoing value.
Capitalize on powerful trends. For extra traction, try to align your business model with prevailing technology, cultural, or economic trends that are shaping the future. For example, the rise of mobile, artificial intelligence, conscious consumerism, remote work, the sharing economy, and urbanization present intriguing opportunities. Where are the shifts happening that your startup could capitalize on?
Read More:
How To Start Business Of Currency Exchange
Network advantages
Take advantage of network effects. Network effects occur when a product or service becomes more valuable as more users adopt it. This makes the offering more attractive, drawing in even more users in a positive feedback loop. Many of today’s leading tech startups harness some form of network effect by nature of their business model and mediated platform. That’s a powerful dynamic to tap into.
Seek out favorable cost and revenue dynamics. It’s advisable to develop a business model with a favorable relationship between costs and revenue. For instance, those with high upfront costs but low marginal costs can drive tremendous profit margins once they hit scale. Digital products and service platforms often enjoy this benefit. Conversely, businesses with high variable costs for each additional sale may struggle.
Plan for defending against disruption. Even the best business models face the risk of being disrupted by new innovations and competitors over time. While being too paranoid isn’t productive, try to bake defensibility and flexibility into your model. That could mean doubling down on proprietary data/IP, emphasizing your strong user community, frequently iterating based on market shifts, or embracing a culture of innovation yourself.
Evolving your startup’s business model over time
Start with the minimum viable business model. Don’t overcomplicate things out of the gate. Start with a lean, simple business model focused on your core value proposition and key revenue stream. You can add nuance, new revenue streams, new customer segments, and other layers of complexity once your core model is validated.
Leverage fast, frequent experimentation. Make hypotheses about the different components of your model, then test those assumptions through fast, low-cost experiments. Pilot new pricing schemes, target new segments, try new channels, etc. and analyze the results. Constantly iterate the model based on those learnings.
Draw insights from data and customer feedback. Let hard numbers and direct customer input drive your optimizations. Dig into usage metrics, cohort data, conversion rates, survey responses, and revenue figures to pinpoint which parts of your model are working well and which need adjustment. And never stop listening to your customers.
Allow for modular, two-sided
Zoom out to spot external disruptions. On a regular cadence, take a step back and audit your business model in light of the broader market landscape. Is new competition emerging? Are new technologies disrupting your space? Is a regulatory shift on the horizon? If so, you may need to pivot or evolve your model.
Allow for modular, two-sided, or multi-model designs. Many successful companies don’t operate off one monolithic model; rather, their business models incorporate certain degrees of flexibility, adaptation, and diversity. Modular designs let you mix-and-match components tailored to each use case. Two-sided models account for multiple constituencies (e.g. users and advertisers). Multi-model approaches optimized for different customer segments or product lines.
Online Services selling business
Stay open to entirely new models. In rare cases, you may need to rip up the playbook and adopt an entirely new model as your startup matures and scales. Netflix started by mailing physical DVDs but later transformed its model to streaming video. Amazon began by selling books online but now generates over half its revenue from AWS and other model expansions. Always be willing to reimagine your model.
The process of creating a winning, sustainable business model for your startup is never finished. It requires diligent ongoing effort: initial blueprinting, keen observation, creative experimentation, and adaptability. The startups that dedicate themselves to this process stand the best chance for long-term success.
FAQs
What are the key components of a startup business model?
The 9 key components are customer segments, value propositions, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, key partnerships, and cost structure.
How can I develop a compelling value proposition?
Focus on clearly defining the core problem you solve and the unique benefits you offer customers. Differentiate yourself from existing alternatives.
Should I prioritize recurring revenue streams?
Yes, recurring revenue models like subscriptions are preferable over one-off transactions, as they provide more predictable, reliable income over time.
How can I make my business model defensible long-term?
Emphasize proprietary data/IP, strong user communities, a culture of innovation, and the flexibility to adapt as your market evolves.
When should I evolve or change my business model?
Continuously test assumptions through fast experiments, analyze data/user feedback, monitor external disruptions, and don’t be afraid to pivot or reimagine your model.
Conclusion
Creating an effective, sustainable business model is a crucial early step for any startup. It involves carefully mapping out how you’ll deliver value to customers and capture a share of that value as revenue. While it takes serious upfront work, a well-designed model provides a blueprint for profitability and future growth. Expect to continuously iterate and evolve your model through experimentation and agile adaptation as your startup matures. Staying nimble and open to change with your model is key to long-term success in today’s rapidly shifting landscape.














1 thought on “How To Create A Business Model For A Startup”